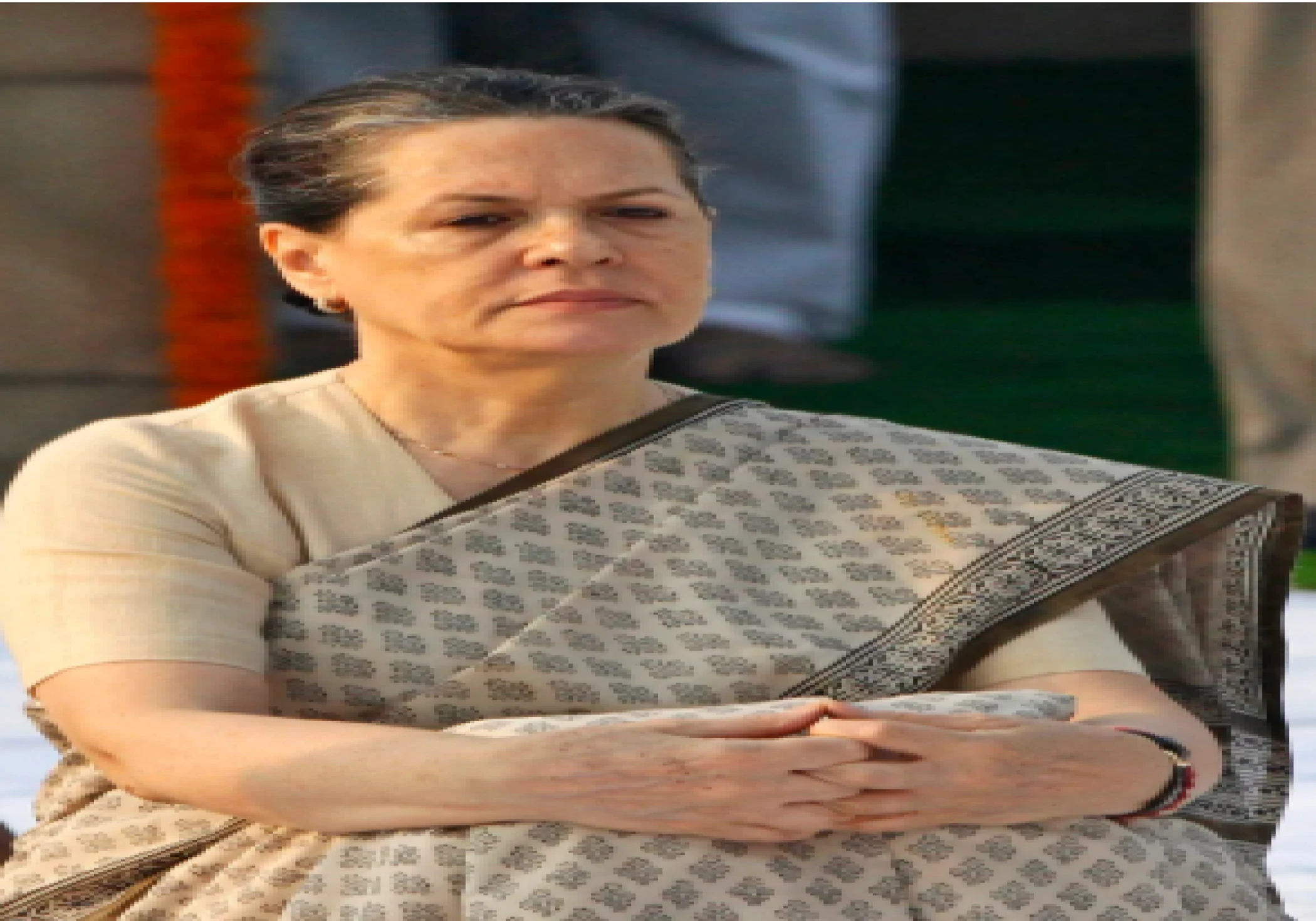
Sonia Gandhi, born Edvige Antonia Albina Maino on 9 December 1946 in Lusiana, Veneto, Italy, has been one of the most powerful and longest-lasting political personalities in India over the last several decades.Her transition from a secluded, private life in Italy to the forefront of Indian political leadership is one of inspiring and towering proportions.Being the widow of India's former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and matriarch of the Nehru-Gandhi dynasty, Sonia's political life is inextricably entwined with India's changing political landscape of contemporary India.
Early Life and Family
Having been born and raised in a conservative Roman Catholic family, Sonia Gandhi was educated in Italy and later went to the UK for further studies. It was there in Cambridge that she met Rajiv Gandhi, a student at the University of Cambridge then, with whom she married in 1968. Sonia moved to India to become part of the powerful Nehru-Gandhi family. More than two decades later, she remained out of the political limelight, observing her family and cultural integration in India.
Political Career
Rajiv Gandhi Premiership (1984–1990)
Following the assassination of Indira Gandhi in 1984, Rajiv Gandhi became Prime Minister of India.Sonia continued to stay in the background, further keeping away from active politics. But when Rajiv was assassinated in 1991, there was a general call within the Congress party for her to take the reins. She declined at first, opting to back the party from behind the scenes instead.
Political Debut and Congress Presidency (1991–1998)
In 1998, following the decline of the Congress party and the disintegration of its leadership, Sonia Gandhi formally joined active politics. Barring doubts about her foreign origins, she was chosen as the President of the Indian National Congress in the same year. Her leadership soon infused new life into the party's organization and ideology, restoring Congress to political viability.
Leader of the Opposition and UPA Chairperson
During the 1999 general election, Sonia Gandhi defeated Amethi, the seat of Gandhi family influence, and became Leader of the Opposition in the Lok Sabha. Sonia's most iconic political moment came in 2004 when she piloted Congress-led United Progressive Alliance (UPA) into office against sitting NDA government. Although overwhelmingly predicted to assume the office of Prime Minister, Sonia Gandhi refrained from becoming the Prime Minister amidst controversy relating to her foreign birth. Instead, she nominated Dr. Manmohan Singh, a well-trusted economist, as Prime Minister, and became UPA Chairperson.
Throughout her tenure, she spearheaded the implementation of pathbreaking social policies such as the Right to Information Act and MGNREGA under the National Advisory Council (NAC), which she headed.
Later Years: Rajya Sabha and Political Transition
Following another Congress victory in 2009, Sonia's political power began to decline after 2014, when BJP swept to office. Over the next few years, she stepped back from front-line politics gradually, handing over party president's gavel to her son Rahul Gandhi. She has since worked as a senior advisor and member of the Rajya Sabha, still guiding Congress policy-making in the background.
Personal Life and Public Perception
In spite of her foreign roots, Sonia Gandhi is universally admired for her poise, dignity, and grit in Indian public life. Her resilience in the face of personal tragedy—the loss of her husband Rajiv and mother-in-law Indira Gandhi—has defined her political image as a firm and unshakeable leader. Having learned Hindi fluently and being deeply entrenched in Indian culture, Sonia continues to be an icon of strength and determination.
Honours and Recognition
Sonia Gandhi has been internationally and nationally recognized for her leadership over the years. In 2007, she was ranked by Forbes as one of the world's most powerful women. Though she never held a formal government office, her indirect influence in Indian politics has been immense. She is also credited with maintaining the ideological core of the Congress party as well as fighting for inclusive, welfare-based policies in the UPA years.
Sonia Gandhi’s political journey, though initially marked by reluctance, has evolved into a saga of determined leadership and influence. Her legacy continues to be debated and discussed, making her one of India’s most iconic political personalities.